Satellite skills and knowledge for operational meteorologist
Listed here are other resources related to Satellite skills and knowledge for operational meteorologist tag:
Note: click on an image to open the Resource
Andreas Wirth shows the benefits and drawbacks of new RGBs that are now possible with FCI and how to use them.
Besides better temporal and horizontal resolution, the FCI sensor on-board MTG-I also offers additional spectral bands mainly in the short infrared and visible range. These new channels were used to create RGB composite images such as the Cloud Type RGB, the Cloud Phase RGB, the Fire RGB and the True Color RGB. This presentation will highlight the benefits coming from these new RGB types. Application examples will be given and the impact of the new channels will be explained. The focus of this presentation will lay on the information provided by the new RGB types as well as on the limitations and challenges forecasters are confronted with when using them.
Roxane Desire gives a complete overview on the new Cloud Type RGB.
While it may seem simple to use at first glance, with its very distinctive and contrasting colors, the Cloud Type RGB product is nonetheless full of subtleties. A review of everything it is capable of and a comparison with other products.
Johan Strandgren talks about the EUMETSAT Level-2 Products.
This presentation outlines the MTG-I FCI Level-2 (L2) products generated at the EUMETSAT Central Facility and disseminated to users. These products support applications such as cloud analysis, atmospheric instability, fire detection, atmospheric motion vectors, and all-sky radiances, serving data assimilation, nowcasting, and research communities. We will present early validation results from the ongoing L2 commissioning and plans for future enhancements.
Carla Barroso gives a presentation on EUMETSAT data visualization resources and repositories.
Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) imagery can be easily explored using EUMETView, EUMETSAT’s user-friendly web-based visualisation tool. Users who wish to go beyond visual inspection can access EUMETSAT's flexible portfolio of data services. One of these is the Data Store, which enables users to easily locate and download both near-real-time and historical datasets. This presentation will begin with a brief overview of EUMETView, followed by an introduction to several Jupyter notebooks designed to bridge the gap between data discovery and practical application. The first notebook focuses on the process of accessing and downloading data from the EUMETSAT Data Store, while the subsequent notebooks delve into the exploitation and visualisation of data from the Flexible Combined Imager (FCI) and the Lightning Imager (LI) sensors on board MTG.
Hans Peter Roesli talks about a new product for low level moisture detection using the new 0.9 channel present on the FCI instrument.
Go to lecture slides
Sven-Erik Enno talks about the Lightning Imager instrument onboard MTG-I1 satellite.
The Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) Lightning Imager (LI) was declared operational on October 31, 2024. This brand-new European Instrument is devoted to the real-time monitoring and characterization of lightning activity over Europe, Africa, and a large portion of the Atlantic Ocean. This presentation will demonstrate LI observational capabilities from individual lightning flashes to hemisphere-scale statistics and present the outcome of the latest LI performance assessments.
Go to lecture slides
Vesa Nietosvaara gives an overview on the MTG programme and discusses FCI instrument and it's uses onboard the MTG-I1.
The complete constellation of Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) consists of three spacecraft: two imaging satellites and one sounding satellite. The first imaging satellite, MTG-I1 is now operational under the name Meteosat 12. The satellite carries two important instruments – Flexible Combined Imager (FCI), a successor of SEVIRI on MSG, and a Lightning Imager (LI), the first space-based instrument monitoring lightning occurrence over Europe, Africa and South America from geostationary orbit. In this talk, we will focus on the FCI and how it can help monitoring the weather and improving nowcasting. Forecasters will now be able to track the development of storms in near-real time with better accuracy, issue more precise and timely warnings about severe and dangerous weather events but also monitor fog development and dissipation, dust outbreaks, forest fires and many other features.
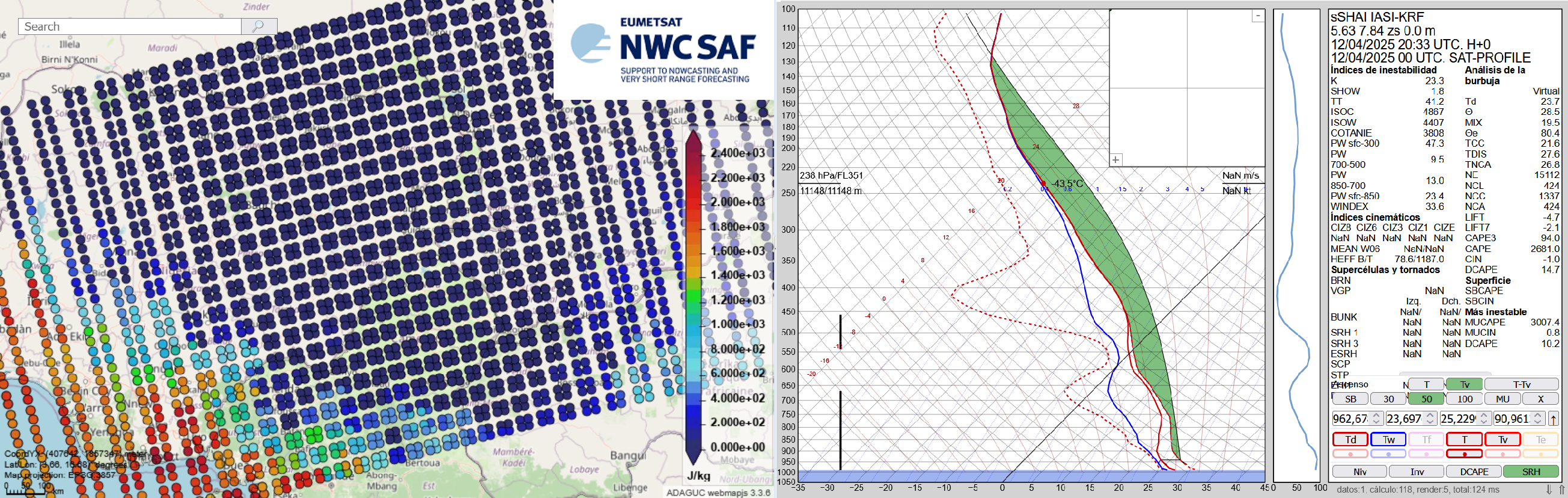
The Nowcasting SAF is planning a new software package dedicated to the new geostationary MTG-S Infrared Sounder instrument (IRS). This new software package will generate Satellite Humidity And Instability products (sSHAI) that will be key in Nowcasting using the IRS instrument. It will also deliver services to make the best use of MTG-IRS channels and combine its virtues with those of the MTG imager FCI.
In this Workshop you will learn about these revolutionary product and services. You will also have a taste of what will come in a few months with MTG-IRS by using in real world applications the prototype product obtained from the polar orbiting IASI instrument.
The Workshop is comprised of 4 presentations:
Part 1. X. Calbet (AEMET) - Introduction GEO-S
Part 2. N. Peinado-Galán (AEMET) - sSHAI prototype
Part 3. N. Peinado-Galán (AEMET) and X. Calbet (AEMET) - Practical cases with course attendants using SHAI on the EWC
Part 4. Miguel-Ángel Martínez (AEMET) - Other services from the GEO-S package: quickIRS, sSHAI_ES and Remapping tool
This document summarizes how to create a new RGB scheme and how to adapt an existing RGB for a new imager.
RGB images can be composed in many different ways. To avoid ambiguity and incorrect interpretations, WMO and EUMETSAT work to standardize the RGB images used by weather forecasters. Experts develop optimized methods to create RGB images that provide high quality visual information about specific features. The use of these standard RGBs helps meteorologists easily understand each other. The standard RGBs have schemes, or recipes, describing how to create them.
Learn more about:
- cloud classification scheme
- recognizing cloud types in satellite imagery
- a satellite product that provides cloud type information
- how cloud top temperature is derived from radiation measurements by satellite sensors
- when and where cloud top temperature provides valuable information to the forecaster
This module covers two different topics. In the first part, the module introduces Luke Howard's cloud classification system and tries to answer the question of whether cloud type classification is possible from space. The second part introduces the concepts of long- and short-wave radiation and how they are used in remote sensing and explains how temperature information is derived from radiation measurements. The module closes with examples of how cloud top temperature information is used in meteorology.
To access the resource click here.
This guide is about the Cloud Type RGB, a new product for European users of GEO satellite data, which can be constructed using data from the Flexible Combined Imager (FCI) on the Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) satellite system. It uses one of the new FCI channels.
At the time the guide was created, FCI was not yet operational, so the characteristics of the FCI Cloud Type RGB were tested using preliminary commissioning data. Similar features were found as with the proxy data. Some examples created from the FCI preliminary commissioning data are presented in this guide.
The main application areas of the Cloud Type RGB are detection of very thin cirrus and higher-level aerosol clouds, and visual differentiation of cloud types, with some limitations. It can also provide some information about areas with dry airmasses.
Training module focusing on identification of volcanic ash and sulfur dioxide plumes from satellite imagery.
Volcanic eruptions have a severe impact on human health, economy and traffic. They regularly cause natural disasters such as tsunamis and lava flows that are difficult to predict. Volcanic eruptions emit large amounts of gases, ash, and other aerosol particles into the atmosphere. In the short term, volcanic ash plumes have serious impacts on aviation. It is, therefore, very important to monitor the extent, height and duration of such events to properly estimate the impact of eruptions at various spatial and temporal scales, using data from different instruments on different satellites.