Weather
In this training module, you get an overview on the life cycle of Upper-Level-Lows and you will learn more about the impact on local weather.
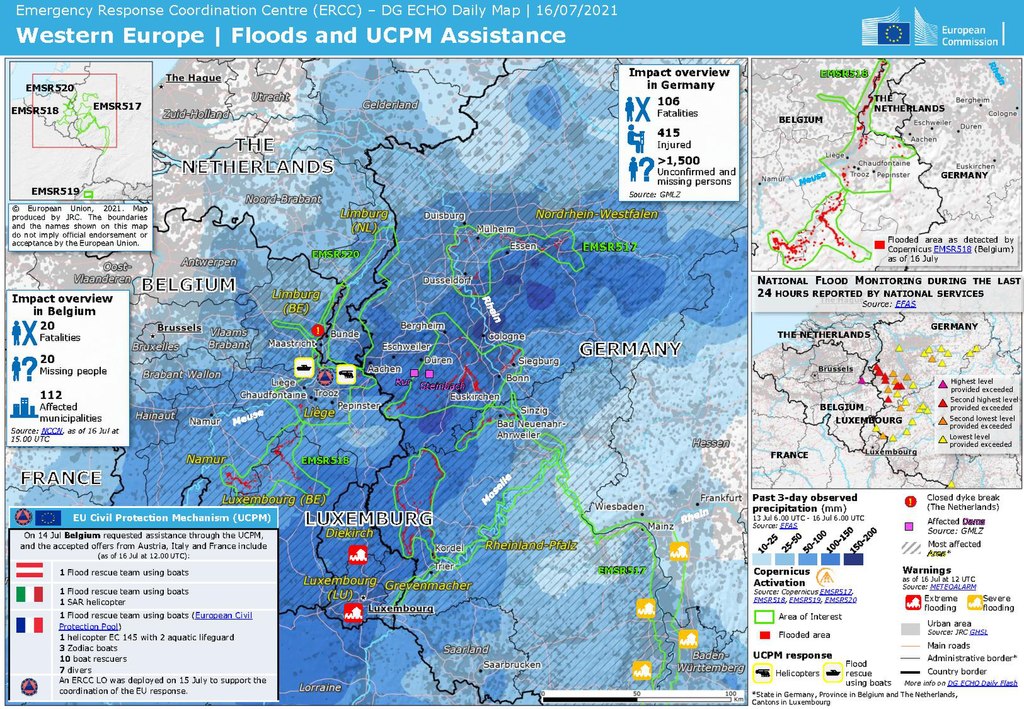
Upper-Level-Lows (ULLs) are a very common phenomenon in mid-lattitudes. They are usually associated with cold and rainy weather that can last for several days. When they remain stationary over a period of time, the can bring considerable amounts of rainfall locally. This synoptic situation has led in the past to floods and damages in infrastructure as will be show by the example of the Central European Flood in summer 2021.
This training module focusses on the meteorological aspects of ULLs, describes the life-cycle and throws a spottlight on the involved physical processes that accompany this meteorological phenomenon. Each stage of development is exemplified by satellite loops and corresponding NWP parameters. Exercises will help you to check the acquired knowledge.
Marianne Koenig gives a short introduction to some established methods to derive meteorological products from satellite data, including the benefits and downsides of products.
Length: 30 minutes.
The course gives a short introduction to some established methods to derive meteorological products from satellite data, including the benefits and downsides of products. Product examples will mainly focus on the MSG products, derived centrally at EUMETSAT and within the NWC SAF project.
Jochen Kerkmann discusses the characteristics of the Dust RGB and presents the challenges of detecting dust clouds (like low level dust at night over water).
Length: 30 minutes.
Dust and smoke detection with SEVIRI RGB products: the lecture focuses on dust and smoke clouds and their identification in RGB products. The first part looks at the solar channels and the natural colours RGB product; the second part presents the triple window IR channels and the resulting dust RGB product. Some challenges of detecting dust clouds (like low level dust at night over water) will be discussed.
Liliane Hofer highlights the properties of the Airmass RGB.
Length: 30 minutes.
The Airmass RGB is for sure one of the more complex RGB composites as it uses brightness temperature differences and not single channels on each colour beam. But - as this presentation will show - it is nevertheless a very powerful tool for discriminating between different air masses and highlighting dynamic properties of the atmosphere.
Maria Putsay talks about how to create an RGB image, how to extract, distill, and package the data into products that are easy to interpret and use for forecasters.
Length: 60 minutes.
What is the benefit to work with RGBs not only with single channel images? How to create an RGB image from raw data? How to create a good RGB image? How to enhance features and which features to enhance? Why use standard RGBs? How to extract, distill, and package the data into products that are easy to interpret and use for forecasters?
Xavier Calbet gives a presentation on MSG absorption channels.
Length: 60 minutes.
CO2 and Ozone channels are difficult to interpret directly because they are not "clean" channels that behave in a simple way. To understand them better, the basic concepts of atmospheric radiative transfer are introduced. In this way, it will be easier to understand how to interpret the meaning of these channels, and by extension, of all the other channels.
Phil Chadwick gives a presentation on the use of WV imagery to analyze and diagnose the 3-D structure and evolution of the atmosphere and meteorological processes.
Length: 60 minutes.
The use of WV imagery to analyze and diagnose the 3-D structure and evolution of the atmosphere and meteorological processes. Real time WV data can provide a high resolution understanding of the atmosphere in time and space that is independent of NWP.
Jan Kanak gives an introduction on the properties of the infra red channels on board of MSG.
Length: 60 minutes.
This presentation deals with the origins of infrared (IR) radiance, with description of different IR spectral regions and selection of spectral bands for meteorological satellites.
In next part practical aspects of utilization of IR satellite data will be presented, from processing fundamentals through image mapping, visualization, practical usage up to recognition and interpretation of various meteorological features. Presentation will explain also how can measured IR radiation provide physical information from different atmospheric layers and how this information can be associated with model outputs. Finally some notes on anisotropy of Earth-Atmosphere system in IR window will be demonstrated on real comparison of simultaneous measurements of the same scene but from different satellite positions in space.
Jose Prieto gives an introduction on the properties of the solar channels on board of MSG.
Length: 60 minutes.
Meteosat solar channels are fantastic, and after 11 years of operation still largely untamed. Additional four solar channels are recruited for the next generation, from 2018, for an eight-a-side match against the infrared team. Have you ever seen midnight sunglints, fire traffic lights or fog dips? Google will not help you. This presentation might cast solar light on those concepts.
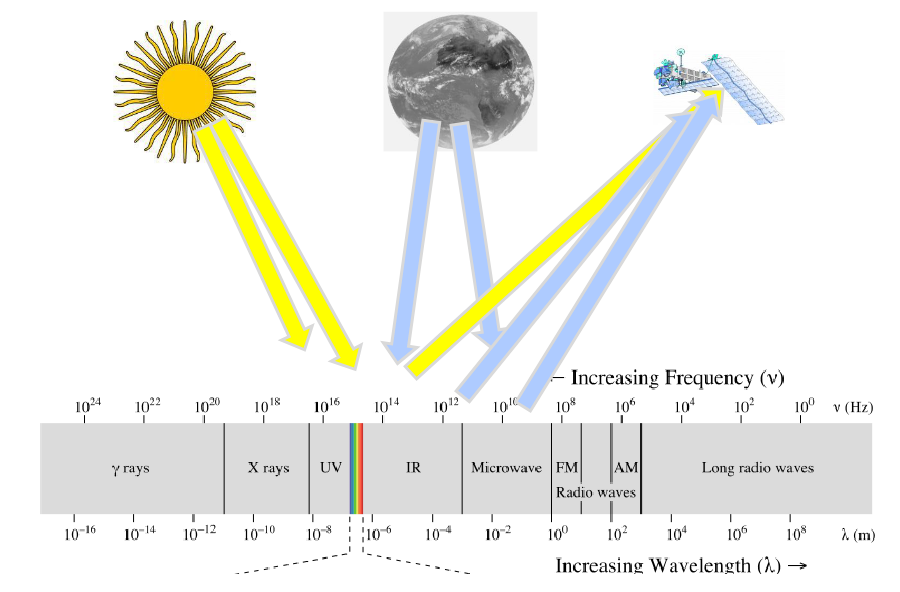
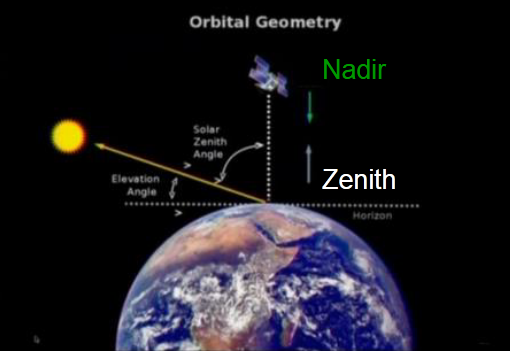
Marianne Koenig gives an introduction to radiation and remote sensing principles. The focus here is on radiation in the infrared and solar spectral range.
Length: 60 minutes.
The course gives an introduction to radiation and remote sensing principles: Questions like “what is remote sensing?”, “what is the electromagnetic spectrum?” and “which physical radiation laws describe all this?” are addressed. We then go into the specific application of all this to the earth-atmosphere system. The focus here is on radiation in the infrared and solar spectral range, as this is used in imaging instruments. Processes like absorption, emission, scattering and reflection will be described. In the end, a short outlook to (infrared) hyperspectral data will be provided.
Andreas Wirth gives an overview on the historical development of satellites, instruments and remote sensing scanning techniques.
Length: 30 minutes.
This lecture presents an overview on the most commonly used instruments on board geostationary and polar orbiting satellites. The focus is laid on similarities and differences of instrument characteristics between these two types of satellites. Different types of instruments, covering the meteorological relevant spectrum, are shown. Active and passive instruments are explained as well as the presently used scanning principles.
Jochen Kerkmann gives an overview on the historical development of satellites, orbits and instruments.
Length: 30 minutes.
The invention of weather satellites has opened a new area in weather forecasting. Satellite observations enable to continuously monitor the weather regimes on the whole globe. Therefore they provide a powerful tool in weather forecasting. This lecture leads from the invention of weather satellites to the current operational satellites.