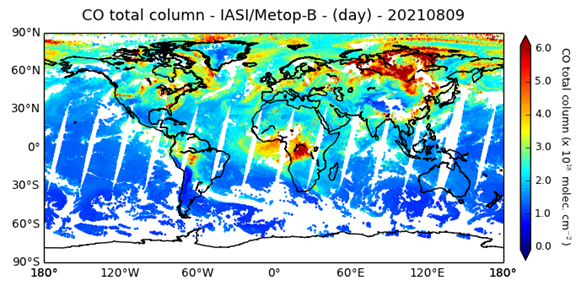
Identify and interpret atmospheric phenomena
Zsofia Kocsis goes over the priniciples of RGB imagery, reasons for its use and guidelines for their creation.
This presentation covers what are the benefits of working with RGBs compared to single channels satellite data. We will cover how we can create RGBs, what makes an RGB good and we will also talk about what are the standard RGBs and why we like to use them.
Lecture slides
Andreas Wirth goes over the topic of Dust Infused Baroclinic Storms (DIBS) and explains the current forecast model inconsistencies regarding DIBS as well as their impact on weather.
Dust Infused Baroclinic Storms (DIBS) have a high impact on weather. Mineral dust particles in the atmosphere reduce sunlight at lower levels, reduce visibility and damp daily temperature maxima. Dust particles can have an impact on forecasted precipitation too, and in higher concentrations, dust particles can cause respiratory problems.
This presentation focuses on circulation pattern that causes dust transport towards Europe and on how to detect high dust loads in- and outside clouds from geostationary satellite imagery on the basis of recent examples.
Lecture slides
In this air quality module, you will learn to respond better to air pollution and Sahara dust events, by learning which resources to use for these events.
Atmospheric composition can be observed using various instruments (satellite and ground-based) and can be analysed and forecasted using numerical models. This training module provides an overview of available online resources that can be used to assess an air pollution or a Sahara dust event. An air pollution event is defined as a time during which the concentration of atmospheric pollutants exceeds air quality standards. In southern Europe, these also include Sahara dust events, which occur mostly in spring and summer, when south-westerly flow transports desert dust from the areas south of the Atlas Mountain range.
Sylvain Le Moal talks about use of lightning data at Meteo France.
Meteo-France already has experience processing data for French overseas territories from next-generation satellites currently in operation, such as United States’ geostationary satellites. The Goes series weather satellites (Goes-16, -17 and -18), and the on-board Geostationary Lightning Mapper (GLM), have now been operational for several years. The GLM detects and maps total lightning – in-cloud, cloud-to-cloud, and cloudto-ground – continuously over the Americas and adjacent ocean regions. The performance of the GLM, the application and use of its data can be produced for forecasters, medias, and numerical weather prediction models.
Nicolau Pineda talks about the new LI and comparison between ground based and satellite based lightning measurements.
The Meteosat Third Generation Lightning Imager (MTG-LI) is now providing continuous optical observations from the lightning occurring in Europe and Africa. Prior to the MTG-LI, the Lightning Imaging Sensor (LIS) onboard the International Space Station (ISS) offered a unique opportunity helping to prepare for the MTG-LI, since it has a similar detection principle. Whereas optical imagers like the ISS-LIS or and the MTG-LI use a narrow spectral infrared emission (777.4 nm) associated with hot lightning intra-cloud channels, commercial ground-based Lightning Location Systems (LLS) detect radio emissions in the low / very low frequency range to locate cloud-to-ground lightning. Therefore, differences between sensors and location techniques must be kept in mind when comparing lightning measurements from different systems. In this regard, the Lightning Mapping Array (LMA), which mostly detects intra-cloud discharges in the VHF range, is best suited for CalibrationValidation purposes.
Bartolomeo Viticchie talks about the new Lightning Imager on the MTG.
Ivan Smiljanic shows how to detect low level moisture with the FCI.
This talk will provide insights into how FCI instrument can be used to detect moisture in the layers close to the surface. Up until the introduction of FCI instrument, the concept of low-level moisture estimation, using solely data from imagers on board GEO satellites was to high degree limited to so-called split window difference (e.g. SEVIRI BTD12.0-10.8). Perhaps the biggest down side of this approach is the fact that BT difference relies heavily on the vertical temperature profiles of the atmosphere (the temperature of moisture level). With introduction of water vapour absorption channel in the NIR spectral region this dependency is avoided. Hence the novel NIR0.91 FCI channels is seen as one of the crucial tools for nowcasting of severe storms, i.e. assessment of pre-conditions and moisture feeding dynamics of convective systems.
Federico Fierli shows how to use satellite imagery for observing aerosol.
Aerosol particles are a key component of weather and climate atmospheric system. Satellite offer the unique advantage to provide a global view with a long-term continuity. We will explore the methods to retrieve aerosol burden with the associated uncertainties for several cases as dust plumes and wildfire emissions. The presentation addresses the data chain from retrieval using different orbital geometries, spectral regions and geophysical products to advanced products as Climate Data Records to the assimilation process.
Lecture slides
Cloud Phase RGB is a new product for European users of GEO satellite data, which can be constructed using data from the Flexible Combined Imager (FCI) on the Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) satellite system. The aim of this RGB is to provide improved microphysical information on cloud tops, in particular discrimination between thick water clouds and thick ice clouds, and cloud top particle size.
This extended guide is about the Cloud Phase RGB, a new product for European users of GEO satellite data, which can be constructed using data from the Flexible Combined Imager (FCI) on the Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) satellite system. It uses one of the new FCI channels, not available with the SEVIRI instrument. This document is an extended guide discussing its characteristics in detail; a quick guide is also available on the EUMeTrain webpage. In this guide, the imagers of Japanese and American geostationary satellites (Himawari/AHI and GOES/ABI) and polar satellites (NPP and NOAA-20/VIIRS) are used to provide proxy data for the FCI.
Identify and locate features indicating regions of possible turbulence.
This module teaches you how to use satellite data to observe and analyze atmospheric phenomena. It will show you which products can be used to identify dust storms, smoke, fires, precipitation, etc.
To access the resource click here.
Note: all resources are provided as an external link which redirects you to https://eumetcal.eu where you will need to create a user account in order to gain access to the course
Identify and locate aerosols and particulate pollution.
This module teaches you how to use satellite data to observe and analyze atmospheric phenomena. It will show you which products can be used to identify dust storms, smoke, fires, precipitation, etc.
To access the resource click here.
Note: all resources are provided as an external link which redirects you to https://eumetcal.eu where you will need to create a user account in order to gain access to the course
Identify and locate moisture features, precipitation types and amounts.
This module teaches you how to use satellite data to observe and analyze atmospheric phenomena. It will show you which products can be used to identify dust storms, smoke, fires, precipitation, etc.
To access the resource click here.
Note: all resources are provided as an external link which redirects you to https://eumetcal.eu where you will need to create a user account in order to gain access to the course