Public weather service
Listed here are other resources related to Public weather service tag:
Note: click on an image to open the Resource
Geir Ottar Fagerlid presents the upgraded Norwegian road weather warning system, focussing on precipitation and wind.
Length: 28 minutes.
Driving and road weather in Norway can be demanding all year around, not just because of the subarctic location, but also because of the complex terrain, from deep fjords to high mountains. The Norwegian Meteorological Institute have recently upgraded its road weather warning system, focusing on precipitation and wind.
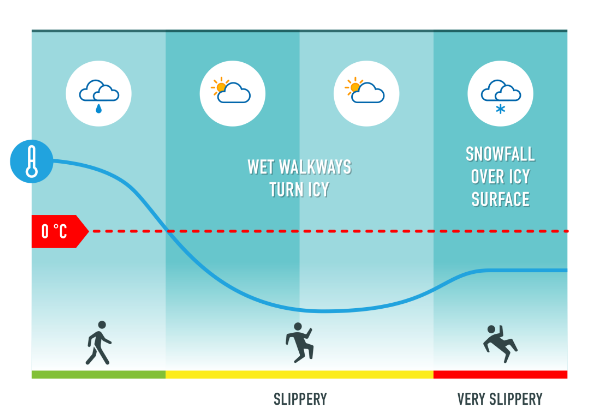
Marjo Hippi presents a numerical model developed at FMI that simulates the level of slipperiness on the side-walks.
Length: 30 minutes.
The Finnish Meteorological Institute (FMI) has developed a numerical weather model that simulates the level of slipperiness on the sidewalks. The model classifies the expected sidewalk slipperiness into three classes; normal, slippery and very slippery. Normal means that there is not ice or snow on the surface. FMI is giving warnings if very slippery sidewalk condition is expected. During very slippery sidewalk condition normal walking is difficult for everyone and extra attention must be paid off when walking.
Icy and snowy sidewalks are very typical phenomena in Finland during winter. Slipperiness due to ice and snow on sidewalks increases the risk of pedestrians' injuries. Almost every second person slips annually in Finland and around 50 000 persons (1 % of Finnish population) are injured and need medical attention. Slip injuries are a big problem causing economic losses and long sick leaves. Emergency departments are crowded during the most slippery days. FMI's warnings for slippery pedestrians' sidewalk condition is one way to improve the safety among the pedestrians and add awareness of slipperiness. Pedestrians may reserve more time for travelling, choose the way of travelling or use anti-slip devices if very slippery pavement condition is forecasted.
Janne Miettinen describes the cooperation between the private company Destia and the national weather service for road maintenance.
Length: 36 minutes.
FMI provides road weather forecasts for all road maintenance companies in Finland that provide maintenance operations for the state. The service is defined by the Finnish Transport Agency, which services and products are included and what are the ways they are delivered.
Addition to this FMI has had a long Public-Private-Partnership (PPP) with the biggest maintenance company in Finland called Destia. At FMI's weather center Destia’s road maintenance supervisors have worked side by side with FMI’s meteorologists for 17 winters. This procedure has been found fruitful for both parties so that we can support each other on road weather related issues. FMI has developed several applications by itself and together with Destia to help operating the maintenance work.
Märt Puust gives an overview on the 4 models used for road weather forecast in Estonia.
Length: 50 minutes.
Since 2016 Teede Tehnokeskus, the state owned road research and consultancy company provides winter road weather information service together with the Estonian Environment Agency (EEA) for all national roads, maintenance companies and Estonian Road Administration. The main service providing tool is a TIK web service https://tik.teeilm.ee/en which includes all essential information for decision making.
Beside the official road weather forecast provided by EEA the service includes also alternative road weather forecasts which are based on regional weather models from Finland, Sweden and Norway and Teede Tehnokeskus own METRo origin road weather model. These four models have been in operation for three winters and a special tool for model comparison and verification has been developed. The presentation gives an overview of the system's architecture and highlights some experiences in integration of Open Data of different sources and createsnew value in relatively large scale.
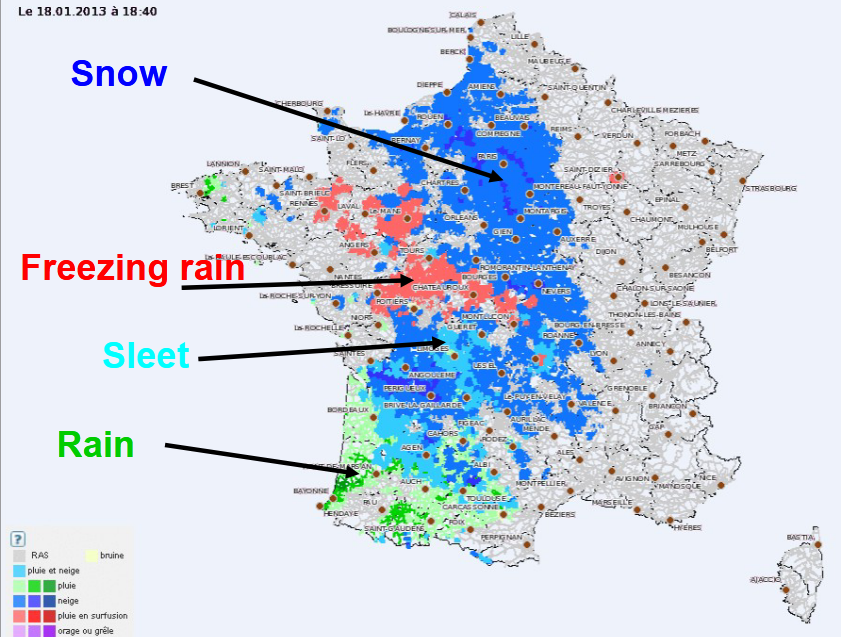
Lovro Kalin focusses on the prediction of freezing rain as an essential factor in road weather forecast.
Length: 26 minutes.
Freezing rain is a relatively complex phenomenon, with rare occurrence but often related to serious damages and threats. With only few tools available, it has always been a strong challenge for the operational forecasters - in terms of appearance, intensity and impacts. Croatia - as well as Slovenia and Hungary - experienced an extreme and disastrous event in winter 2014, with several hundreds million Euro damage, and temporal collapse of the traffic and energy system.
This paper presents recent developments and experiences in freezing rain operational forecasting. A major tool used recently is the new 'precipitation type' product provided by ECMWF, and so far with overall very good performance. It is accompanied by other diagnostic tools defined in the Croatian Hydrological and Meteorological Service. Several recent cases will be presented, and experiences and forecast performance will be discussed.
Three different approaches to forecast road weather at Meteo-France are presented.
Length: 36 minutes.
During winter, snow or ice presence on the road might have serious consequences on road traffic and security and many efforts were done for several years to develop decision-making tools for road management in winter. For this purpose, Météo-France uses, in an operational way a specific system dedicated to the road weatherforecast.
The first one, OPTIMA is a high-frequency (5 min) nowcasting system providing 1 hour forecasting and based on data fusion approach. It is dedicated to real time and short range anticipation of road impacting phenomenon. It was specially developed to work at the road network resolution (5km).
The data OPTIMA uses for the forecast process:
- Radar observation and nowcasting
- Surface observation network and road weather stations observations from customers
- Best available weather forecast (i.e. expertized by human forecasters)
- Specific road weather forecast
As an input for this decision-making tool, Météo-France uses numerical road models, which permit to simulate the behavior of a road under the influence of atmospheric conditions and the behavior of the snow on the road. Since 2012, road models are forced by human expertized atmospheric forecast instead of a direct coupling with numerical weather prediction models. Thissystems, called PEIR (Expertise Predictions for ISBA-Route), are the basis of road conditions forecasting products for French road managers.
Since the beginning of operational road weather forecast in Météo-France, all the products were based on deterministic forecasts, however since 2018/2019 winter, a new approach is tested, based on ensemble forecast.
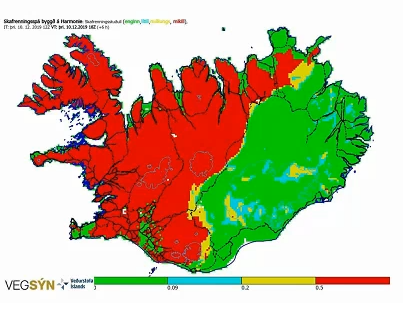
Elin Björk Jónasdóttir introduces the use of high resolution limited area models, SOT and EFI products and specific risk products such as snow drift models.
Length: 35 minutes.
Winter weather in Iceland is severe on any scale. Strong winds, deep synoptic cyclones, blizzards and avalanche risk are conditions that happen every year. The island of Iceland is mountainous and to from one part of the country to another travellers have to cross at least one, and often several mountain passages or drive on roads where steep and high mountains and complex terrain control the winds.
The Icelandic Meteorological Office (IMO) does not do specific road weather forecasts but regular forecasts for all parts of Iceland as well as impact based warnings, where societal impact, including impact on traffic is a part of the evaluation process. In this session I will introduce the use of high resolution limited area models, SOT and EFI products and specific risk products such as snow drift models based on the Harmonie Arome model.
The operational GMS system, which gives forecasts every hour, and is available through a web platform for the regional traffic agencies in Flanders and Wallonia is presented.
Length: 42 minutes.
Forecasting the conditions of roads and highways is important for traffic safety and road maintenance (salting, clearing snow) decision making in Belgium. The Royal Meteorological Institute of Belgium (RMI) collaborated with the Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI) to adapt the KNMI road weather model for Belgian roads. It is based on a 1D radiative transfer model that makes use of meteorological input from different numerical weather prediction models and the INCA-BE nowcasting model used by the RMI weather office. The output (road surface temperature and condition) is generated for about 90 road weather station locations in Flanders and 50 in Wallonia, and is visualized through a GIS interface. We present our operational "GMS system", which gives forecasts every hour, and is available through a web platform for the regional traffic agencies in Flanders and Wallonia. After that, we give a brief introduction to the SARWS project, which RMI participates in with other Belgian partners. Crowd-sourced data is increasingly used in weather science, and road forecasting is no exception. One of the aims of the SARWS project is measuring several weather parameters in real-time from vehicle sensors, in order to enhance the RMI road weather forecasts performed, and eventually send warnings to drivers in case of dangerous conditions. In the presentation, we will highlight the first results of a field test performed by three cars in the region of Antwerp.
Presentation 16 in the Warnings Event Week 2017
Length: 17 min
Author: Tamás Alaga (OMSZ)
Making reliable severe weather forecasts is always a great challenge. Communicating them towards the public and special end users is sometimes greater, even if the forecast is good. Tamás Alaga says that the Hungarian Meteorological Service (OMSZ) plans to develop and simplify its two-level warning system to make it more understandable. The problem is knowing when to stop with these simplifications. Tamás also explains how does the service handle probabilistic forecasts and delivering such forecasts to public and consumers.
Presentation 15 in the Warnings Event Week 2017
Length: 36 min
Author: Kaisa Solin (FMI)
Summer thunderstorm Kiira left a significant trace in Finland in August of 2017. With big forest damages because of strong wind gusts, big number of interventions in southern Finland this case is suitable for analysis and through that presenting the Finnish severe weather follow-up product LUOVA. Kaisa Solin from Finnish Met Service explains LUOVA more in detail in the video.
Presentation 14 in the Warnings Event Week 2017
Length: 22 min
Author: Thomas Turecek (ZAMG)
The presentation is delivered on the basis of the polar air outbreak in mid April 2017 that caused a late winter outbreak in the Alpine area in Austria. Because of that Austrian met service had to reactivate winter maintenance warnings. Thomas Turecek of Austrian Met Service (ZAMG) explains us how did they cope with this event and how are the warnings they issued connected with climatological thresholds for that specific area.
Presentation 13 in the Warnings Event Week 2017
Length: 15 min
Author: Tuomo Bergman (FMI)
ANYWHERE project is a H2020 funded project that aims to develop tools to support coordination of the emergency response operations to face challenge of the extreme weather and climate events. Tuomo Bergman from Finnish Met Service (FMI) tells us that the purpose is to build a pan-European multi-hazard platform for faster analysis and anticipation of the risk prior to event occurrence, improved coordination of the emergency actions and assist to raise the self-preparedness.