Identify and interpret atmospheric phenomena
Jean-Marc Moisselin presents the most recent developments of the NWCSAF convection products.
Length: 30 minutes.
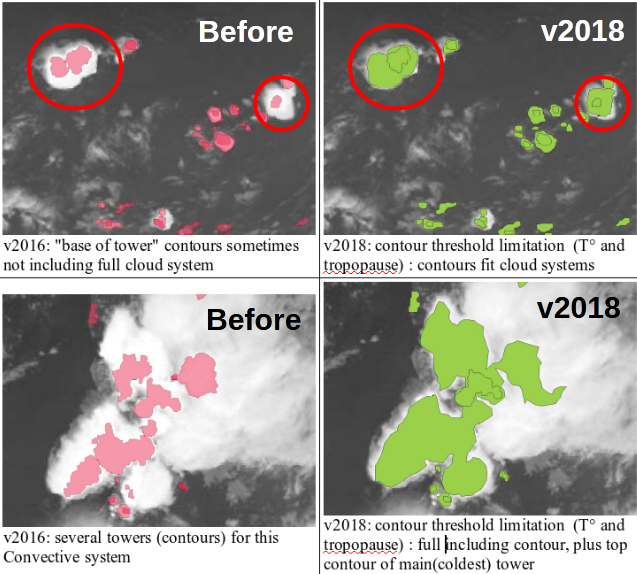
Météo-France develops and contiuously upgrades CI (Convection Initiation) and RDT (Rapidly Developing Thunderstorm) products. Both have been developed in the framework of NWCSAF.
CI is a pixel-based product that provides the probability for a pixel to develop in thunderstorm. The last delivery, v2018, has reached the "pre-operational" status in Eumetsat sense thanks to new developments (e.g. use of microphysics), tuning and validation effort. RDT is an object-based product that aims to detect, track, characterize and forecast the convective cells. Version v2018, includes new features like lightning jumps detection and is highly flexible and configurable. Status is "operational". RDT is very useful for aviation end users.
Georg Pistotnik talks about how convective cells organise to single-cells, multi-cells and super-cells.
Length: 31 minutes.
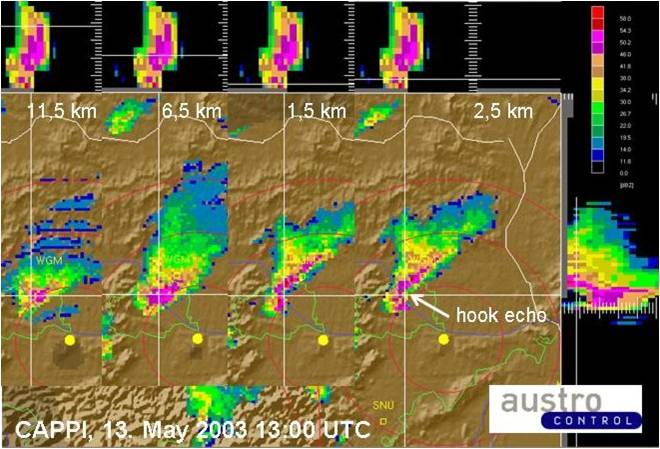
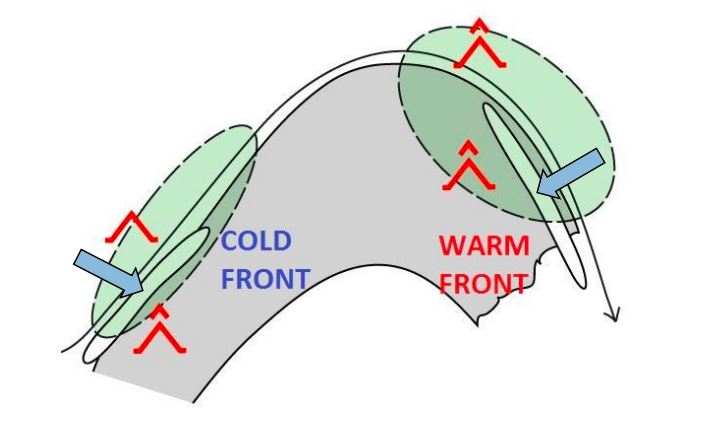
According to their degree of organization, thunderstorms can conceptually be divided into single cells, multicells and supercells. Organized storms, in particular supercells, are responsible for the large majority of severe convective weather like large hail and damaging wind gusts. They are favored by high latent instability and/or strong vertical wind shear and exhibit characteristic behavior in radar and satellite data. For nowcasting purposes and timely weather warnings, it is therefore crucial to recognize organized and severe thunderstorms in remote sensing data. This presentation focuses on key properties of this distinction and illustrates some characteristic examples.
Tomas Pucik investigates the relation between AACP and hail occurrence.
Length: 23 minutes.
Above anvil cirrus plumes (AACPs) have been established in the scientific literature since 1980s. Recent improvements in the temporal and spatial resolution of the satellite data brought back attention to their potential use as an indicator of severity of convective storms. In 2018, we have identified 26 days, where damaging hail reaching at least 5 cm, causing significant economic or societal impact was reported to the European Severe Weather Database. For the selected hailstorm days, where rapid-scan imagery with 5-minute temporal resolution was available, we identified 29 very large (>= 5 cm) hail producing storms. 25 of these hailstorms did show an AACP, but only 12 of these plume producing storms could be clearly identified using the visible imagery. The range of lead time of the AACP appearance to the first hail report was very large and in about half of the cases, the plume occurred only during or after the time of the first large hail report. Due to the limited number of cases, the main purpose of the presentation is, rather than drawing conclusions, to open a discussion on the operational usability of AACPs in warnings for convective storms.
Kris Bedka talks about methods helping to detect hazardous weather situations for aviation.
Length: 30 min
Author: Kris Bedka (NASA)
Current generation geostationary satellites are observing convection that is hazardous to aviation at increasingly high spatio-temporal detail. In recent years, commercial and research aircraft have collected automated turbulence and cloud ice water content observations that can be used to better understand exactly where within deep convection the turbulence and icing conditions are typically occurring. Ground-based weather radar and severe weather reports also identify locations of hail, downburst wind, and tornadoes. Research conducted at NASA Langley Research Center (LaRC), in collaboration with a number of U.S. and international partners, has resulted in geostationary-based analyses and automated detection algorithms that can denote where turbulence, icing, and severe weather conditions are likely. These methods are applicable to any geostationary visible and IR imager across the globe and therefore can be used to map these weather hazards in nearreal time, a capability that is especially valuable over regions without weather radars and other conventional observations of aviation hazards.
Alexander Jann and Andreas Wirth present the new aviation products of ASII-NG (Next Generation).
Length: 30 min
Author: Alexander Jann, Andreas Wirth (ZAMG)
Two new satellite-derived products related to turbulence analysis have been developed recently in the frame of the Nowcasting-SAF. The first product (ASII-GW”Automatic Satellite Image Interpretation – Gravity Waves”) objectively detects grating patterns in the water vapor 7.3 imagery which point to the presence of gravity waves. The second product (ASII-TF “Automatic Satellite Image Interpretation – Tropopause Folding”) identifies the location of tropopause folds from satellite and NWP data. The algorithm is based on the logistic regression method.
In this presentation, we will talk about the selected algorithms and present cases from the official Nowcasting-SAF validation reports (to be released shortly) to illustrate the product performance.
Peter Schmitt analyses the different aspects of CAT and presents a CAT forecasting method.
Length: 40 min
Author: Peter Schmitt (DWD)
Clear air turbulence (CAT) is the term for medium- or high-level turbulence in regions with significant wind shear. CAT is an important factor for the aviation safety.
In the first part of the presentation, I will show you typical parts of CAT in relation with the 300 hPa geopotential analysis. Furthermore you get an overview to the correlation between CAT and characteristic cloud patterns in satellite images. In many cases satellite images provide the first clue or a confirmation for the presence auf CAT.
The second part is dedicated the forecast of CAT in Deutscher Wetterdienst (DWD) with the ICON model. DWD has been applying a forecast method based on Eddy Dissipation Rate (EDR). This real property of atmospheric turbulence is the main sink term of Turbulent Kinetic Energy. In a case study you will see the typical working process in practice with consideration of the model output, typical cloud pattern in satellite image and the use of the conceptual model and the structure of geopotential field.
Lovro Kalin focusses on the prediction of freezing rain as an essential factor in road weather forecast.
Length: 26 minutes.
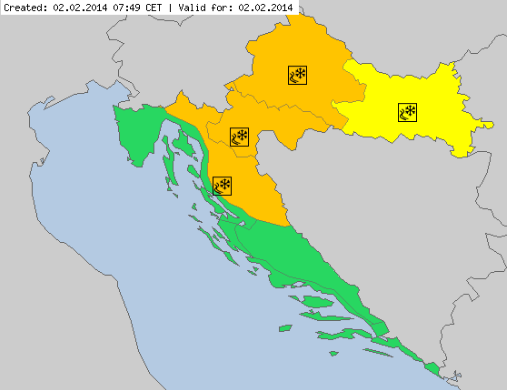
Freezing rain is a relatively complex phenomenon, with rare occurrence but often related to serious damages and threats. With only few tools available, it has always been a strong challenge for the operational forecasters - in terms of appearance, intensity and impacts. Croatia - as well as Slovenia and Hungary - experienced an extreme and disastrous event in winter 2014, with several hundreds million Euro damage, and temporal collapse of the traffic and energy system.
This paper presents recent developments and experiences in freezing rain operational forecasting. A major tool used recently is the new 'precipitation type' product provided by ECMWF, and so far with overall very good performance. It is accompanied by other diagnostic tools defined in the Croatian Hydrological and Meteorological Service. Several recent cases will be presented, and experiences and forecast performance will be discussed.
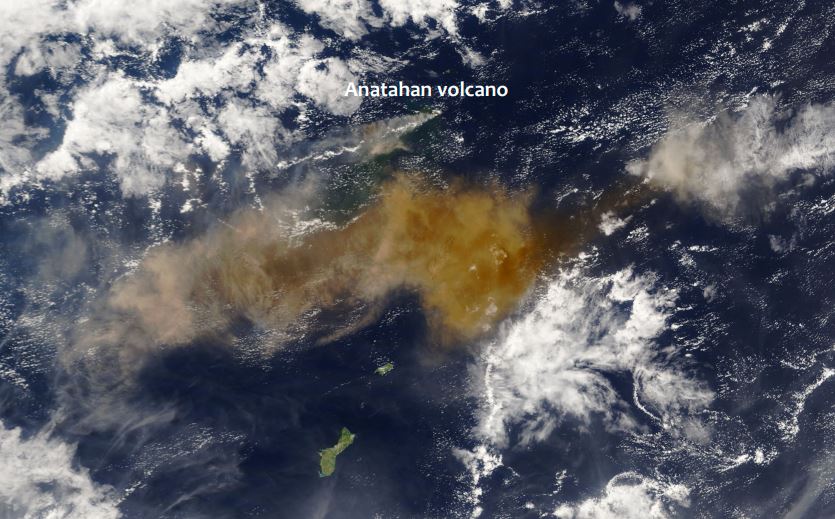
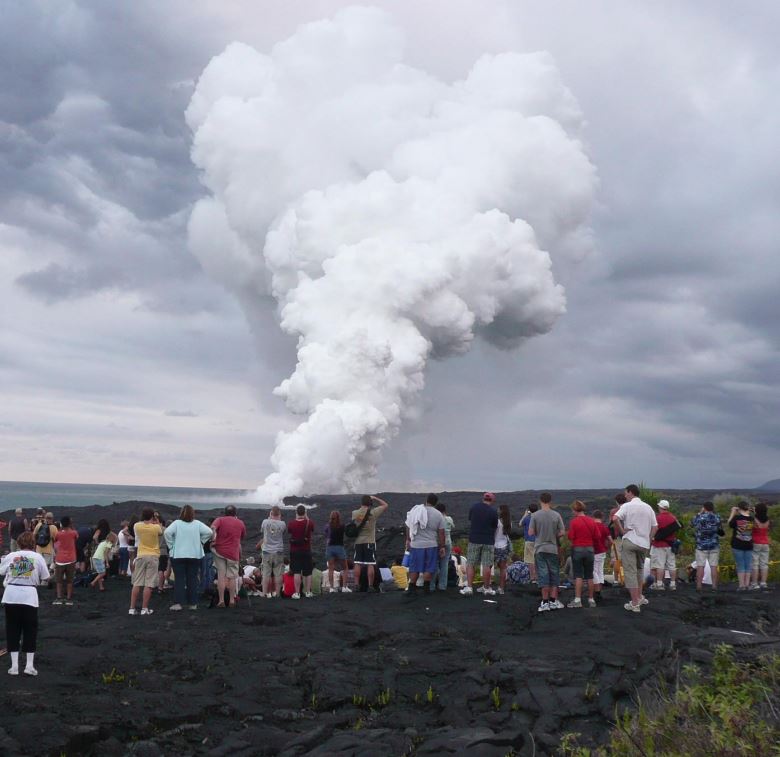
Fred Prata presents a series of volcanic eruption and analyses them from the satellite perspective.
Length: 65 min
Author: Fred Prata (AIRES Pty Ltd)
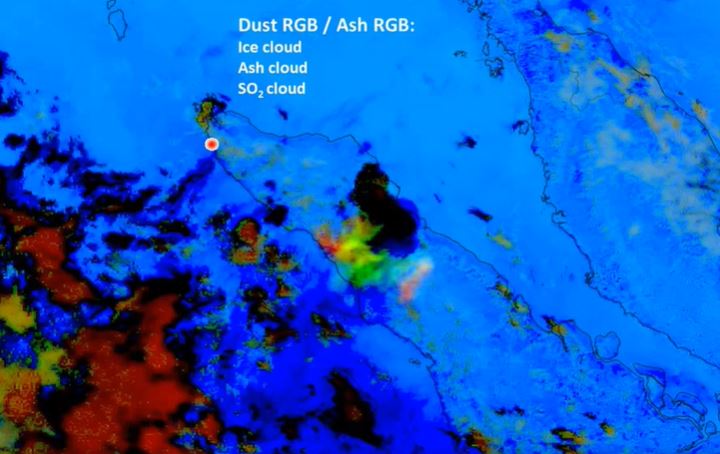
Since the late 1970's earth-orbiting satellites have been able to observe the weather around the globe and provide quantitative information on cloud movements. These data have proved extremely valuable for tracking volcanic ash clouds and more recently allowing quantitative information on volcanic ash column amounts and also on SO2 gas - another potential hazard to aviation. Notable incidents between commercial aviation and ash clouds, several in Indonesia and Alaska, have occurred during the satellite era (~1960's onwards). The talk will cover methods used to identify, quantify and monitor volcanic ash clouds and frame this in the context of the potential hazard.
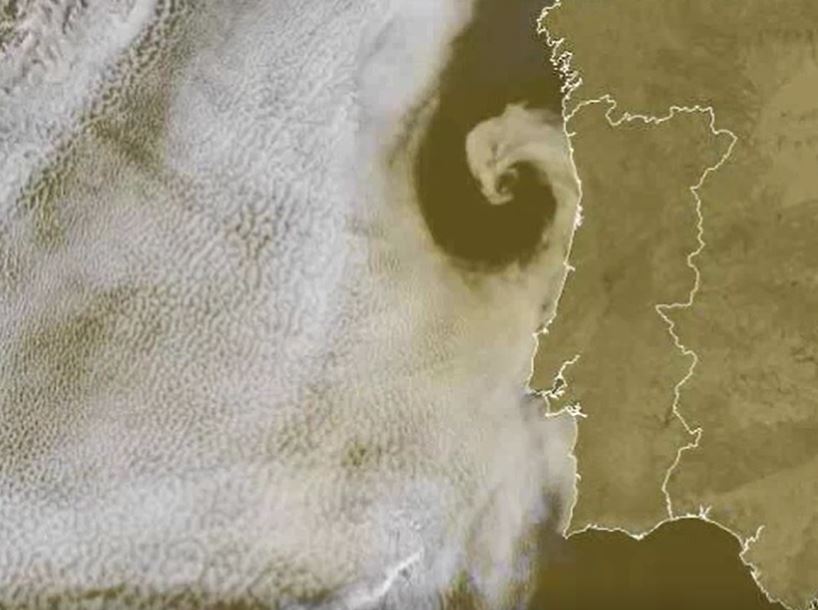
Hans Peter Roesli discusses various satellite pattern observed over the seas.
Length: 40 min
Author: Hans Peter Roesli, Switzerland
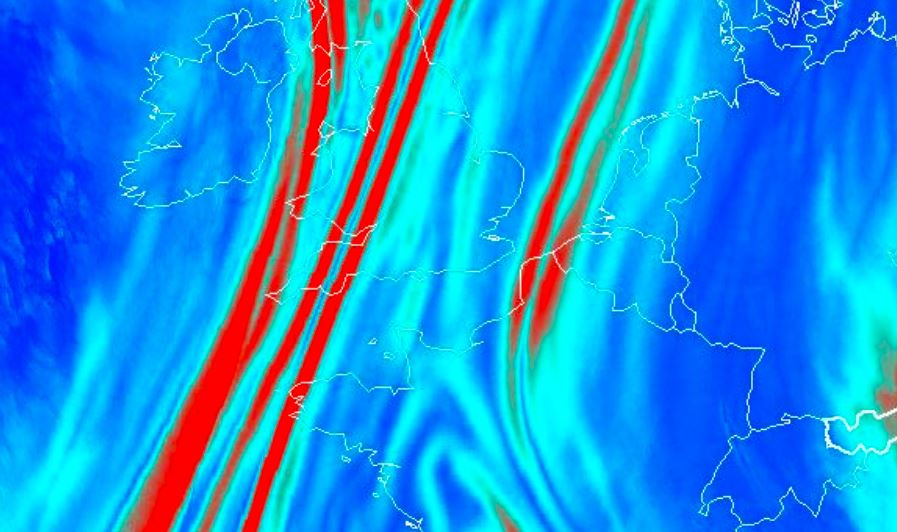
Sea and coastal areas have radiative characteristics that enhance the identification of non-meteorological features like smoke, ash or dust. Maritime inversions and atmospheric interchanges along coastal areas engender particular cloud patterns like Bénard cells, Kármán vortex streets, undular bores, ship trails, (extra) tropical cyclones or sea breeze fronts. Examples of such features will be shown and discussed, using imagery from geostationary and polar weather satellites.
Christian Herold presents case studies in order to give an answer if IASI profiles help predicting sting jets.
Length: 37 minutes.
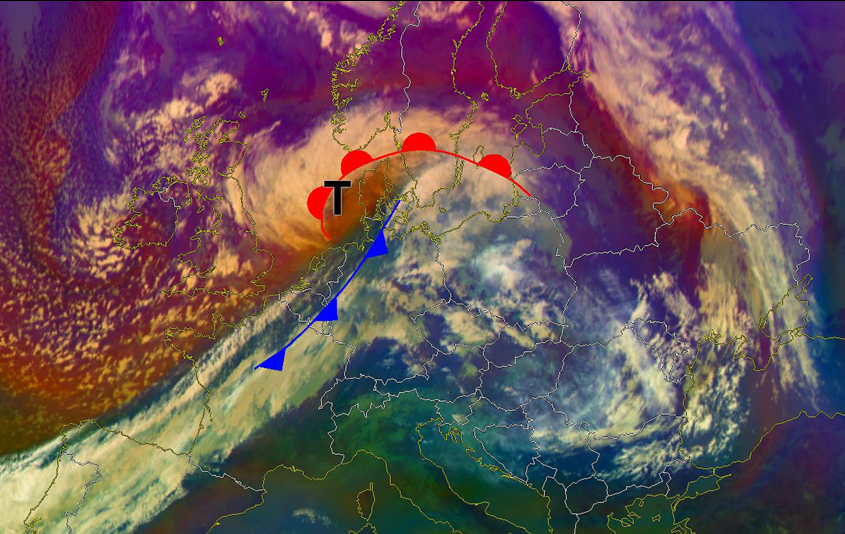
Strong winds southwest of the centre of a Shapiro-Keyser-Cyclone are often associated with a cold conveyor jet or a sting jet. The sting jet is a strong mesoscale flow with a very high damage potential. It is a huge challenge for NWP and forecasters to predict correctly a sting jet. The question is: Can IASI profiles help us for a better prediction of such mesoscale severe wind events connected with sting jets? Therefore, some case studies will be presented.
Length: 67 min
Author: Marko Blaskovic (DHMZ)
Marko Blaskovic goes through all the important atmospheric phenomena you can possibly see using satellite imagery. At the beginning the lecture treats smoke and dust with some examples and exercises. After that, ways of detecting precipitation clouds, analysing convection and pollution are shown in a couple of examples and the presentation then ends with a short overview of clear air turbulence visible from satellites.
Presentation 1 of the Environment Event Week 2016
Length: 30 min
Author: Oleg Dubovik (University of Lille)
The GRASP (Generalized Retrieval of Aerosol and Surface Properties) algorithm has been developed for enhanced characterization of the properties of both aerosol and land surface from diverse remote sensing observations. The overall concept of the algorithm is described by Dubovik et al. (2014), while the detailed are given in the paper is by Dubovik et al. (2011). The algorithm is based on highly advanced statistically optimized fitting implemented as Multi-Term Least Square minimization (Dubovik, 2004) and deduces nearly 50 unknowns for each observed site. The algorithm derives a set of aerosol parameters similar to that derived by AERONET including detailed particle size distribution, the spectral dependence on the complex index of refraction and the fraction of non-spherical particles. The algorithm uses detailed aerosol and surface models and fully accounts for all multiple interactions of scattered solar light with aerosol, gases and the underlying surface. All calculations are done on-line without using traditional look-up tables. In addition, the algorithm can use the new multi-pixel concept - a simultaneous fitting of a large group of pixels with additional constraints limiting the time variability of surface properties and spatial variability of aerosol properties. This principle provides a possibility to improve retrieval for multiple observations even if the observations are not exactly co-incident or co-located. Significant efforts have been spent for optimization and speedup of the GRASP computer routine and retrievals from satellite observations. For example, the routine has been adapted for running at GPGPUs accelerators. GRASP inherits many aspects used in AERONET retrieval. At first GRASP has been developed for POLDER/PARASOL multi-viewing imager and later adapted to a number of other satellite sensors such as METEOSAT/MERIS at polar-orbiting platform and COCI/GOMS geostationary observations. It can be equally applied to ground-based AERONET and lidar observations. The results of numerical tests and results of applications to real data will be presented.