Weather
Presentation 11 in the Warnings Event Week 2017
Length: 28 min
Author: Justyna Wodziczko (MetNo)
The Norwegian Met Service (MetNo) uses a wide variety of social media from Facebook and Youtube to Twitter and Instagram for delivering information to people around the country (and world). That way MetNo can post numerous short news, pictures and general weather information that people find appealing because of their shortness and informativity. On the other hand how are the extreme events reported through such services?
Presentation 10 in the Warnings Event Week 2017
Length: 32 min
Author: Nuno Moreira (IPMA)
Nuno Moreira from Portuguese Met Service (IPMA) is going to show us the current warning system used in Portugal. How are their decisions affected by the impacts that weather may have on wide variety of parameters that can then affect people? Social media are playing an important role in communicating weather information to people nowadays. How to, what and when to communicate certain warnings to people? Nuno will try to answer all of these questions from IPMA's point of view.
Presentation 9 in the Warnings Event Week 2017
Length: 22 min
Author: Barbara Wrona (IMGW)
A case study including three examples of tropical air advection into mid-latitudes is presented by Barbara Wrona from Polish Met Service (IMGW). These protrusions of warm and moist air caused convection and severe convection over a big part of the country. Barbara is going to analyze the latter one from the synoptic point of view and will tell us about the warnings that have to be issued in these cases.
Presentation 8 in the Warnings Event Week 2017
Length: 31 min
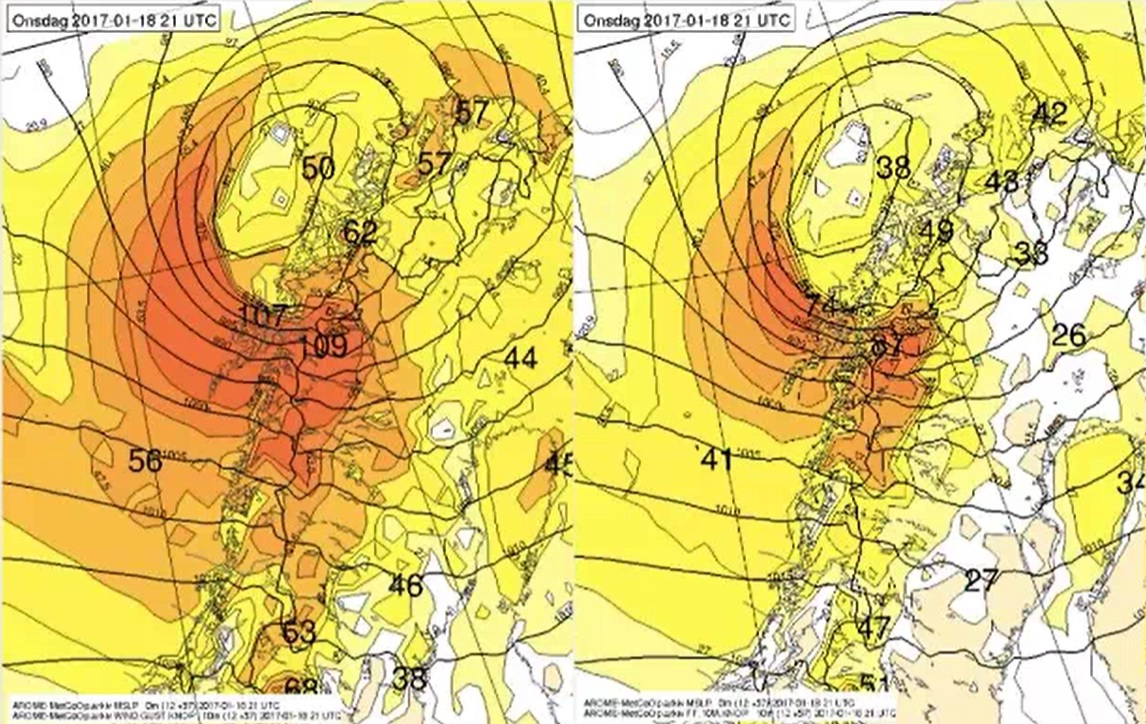
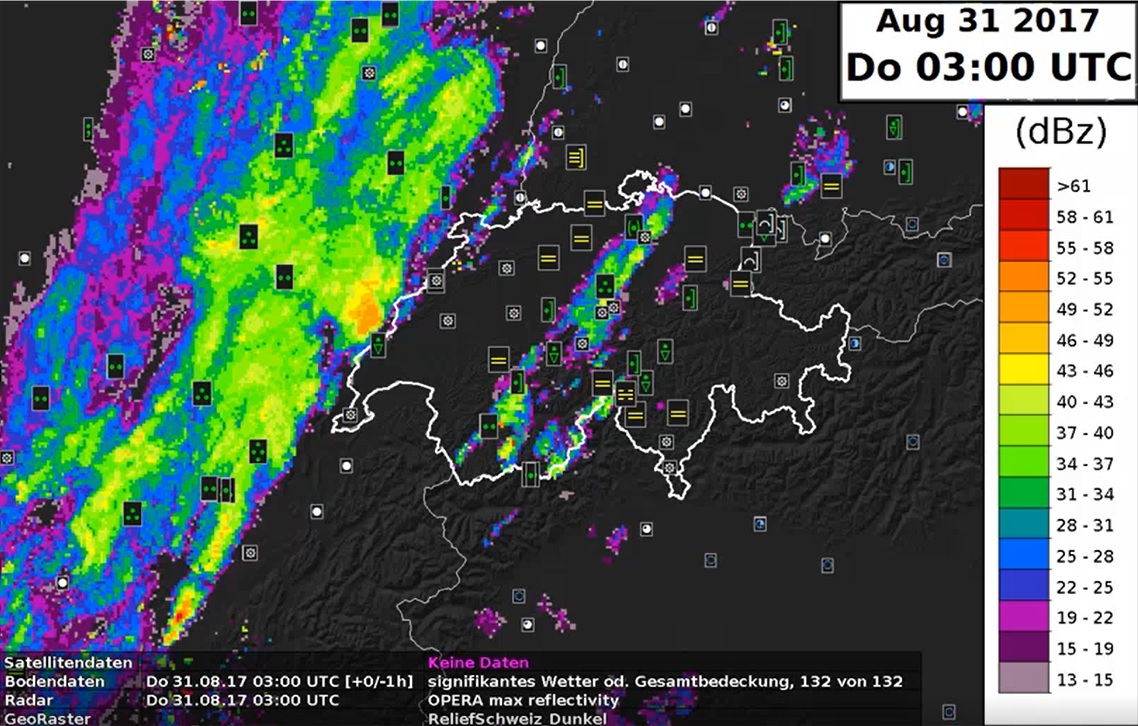
Author: Daniel Murer (MeteoSwiss)
Severe weather warnings at MeteoSwiss started more than thirty years ago, firstly with warnings for heavy precipitation. After the storm 'Lothar' in 2001 warnings for wind, rain and snow have been introduced and then the system was updated in 2009 with new software, NinJo. After this short introduction, Daniel Murer from MeteoSwiss will present us a case that will illustrate the process of issuing warnings and decision making in the Swiss Met Service.
Presentation 7 in the Warnings Event Week 2017
Length: 37 min
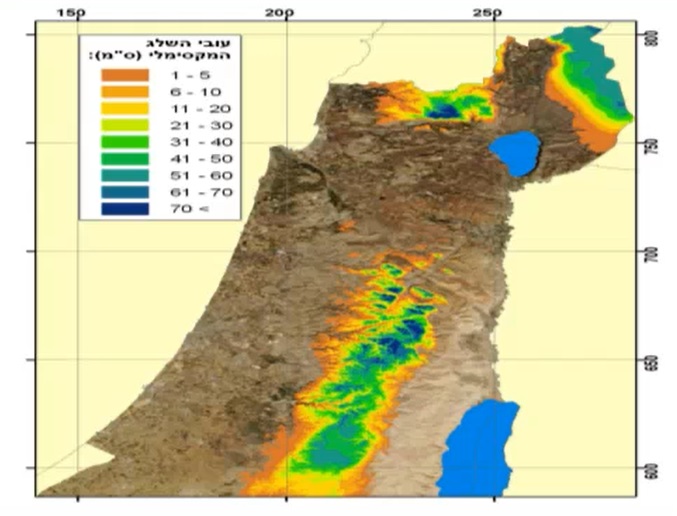
Author: Shay Frenkel (IMS)
Cold lows that bring significant amounts of snow are quite rare in Israel and if they do appear they usually affect the mountainous area of the central part of the country. One such event happened in December 2013 and brought a lot of problems in traffic, power supply and also took lives. Shay Frenkel from Israeli Met Service described the synoptic situation of the event and told us what other tools to use and how did the climatology of the area affect the prediction.
Presentation 6 in the Warnings Event Week 2017
Length: 37 min
Author: Izolda Marcinoniene (LHMS)
Izolda Marcinoniene from Lithuanian Met Service presented us the case study about a severe storm that happened on 11 July 2016 in Lithuania. Tropical air mass usually reaches Baltic states in the summer time and because of it convection develops in the region, but this case deserves a special treatment due to the intensity of the convection that happened. A mesoscale convective system (MCS) developed during the day over Poland and later shifted to Lithuania and Belarus.
Presentation 5 in the Warnings Event Week 2017
Length: 39 min
Author: Ivan Tsonevsky (ECMWF)
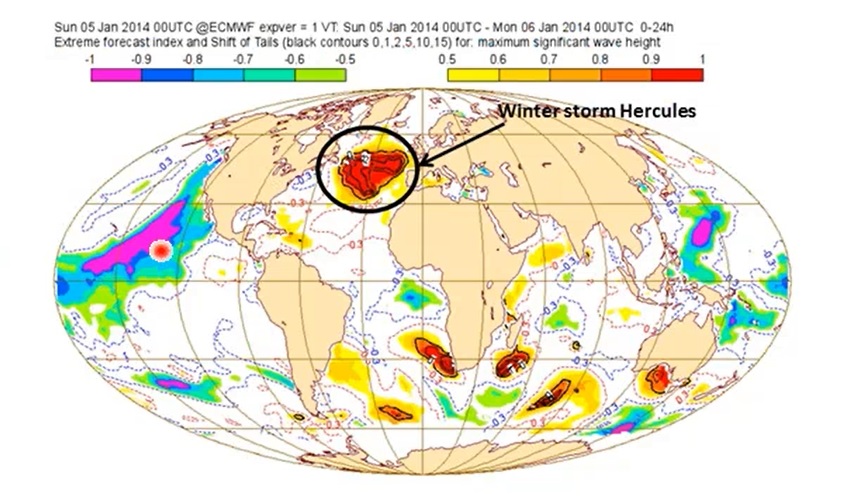
The Extreme Forecasting Index (EFI) and the Shift Of Tails (SOT) index are two operations products developed by ECMWF for usage in forecasting severe weather. The EFI is based on ECMWF ensemble forecasts and it compares these forecasts with the model climate (M-climate) that is generated by the model re-runs. While the high EFI tells us that the confidence level of a forecast is higher for a certain event, the positive high SOT value tells us that the event would be more extreme than the one with low SOT value. At the end Ivan shows us a few cases and demonstrate how EFI and SOT work together.
Presentation 4 in the Warnings Event Week 2017
Length: 44 min
Author: Gernot Zenkl (ZAMG)
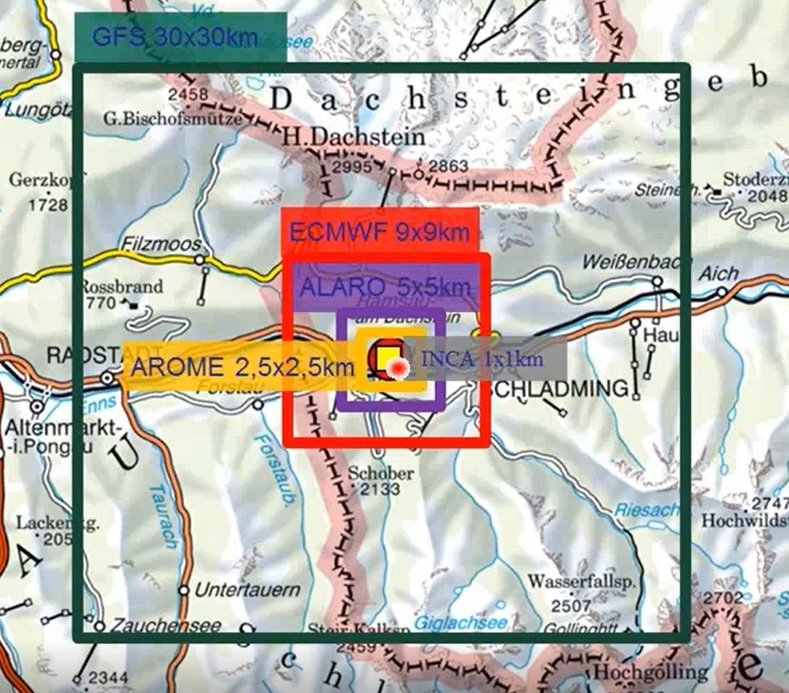
In this presentation Gernot Zenkl presents us the work of avalanche forecasters in the Alpine regions of Austria. He describes us how the stations are maintained, what kind of measurements are done and what models are used for this kind of forecast. In general there are 7 synoptic situations or patterns that affect the Alpine areas and which the forecasters should be aware about. At the end Gernot analyzes three avalanche cases, he describes the damage done, the forecasting and the issued warnings.
Presentation 3 in the Warnings Event Week 2017
Length: 29 min
Author: Lars Kirchhuebel (DWD)
Forecasting winter weather is a challenging job for a forecaster because of snow, ice, freezing rain, fog, etc. In this presentation Lars Kirchhuebel is presenting how are the winter weather situations, especially black ice phenomena, forecasted and warned in Deutscher Wetterdienst and during this walkthrough he will present the black ice case of 7th of January 2017.
Presentation 2 in the Warnings Event Week 2017
Length: 42 min
Author: Marcus Beyer (DWD)
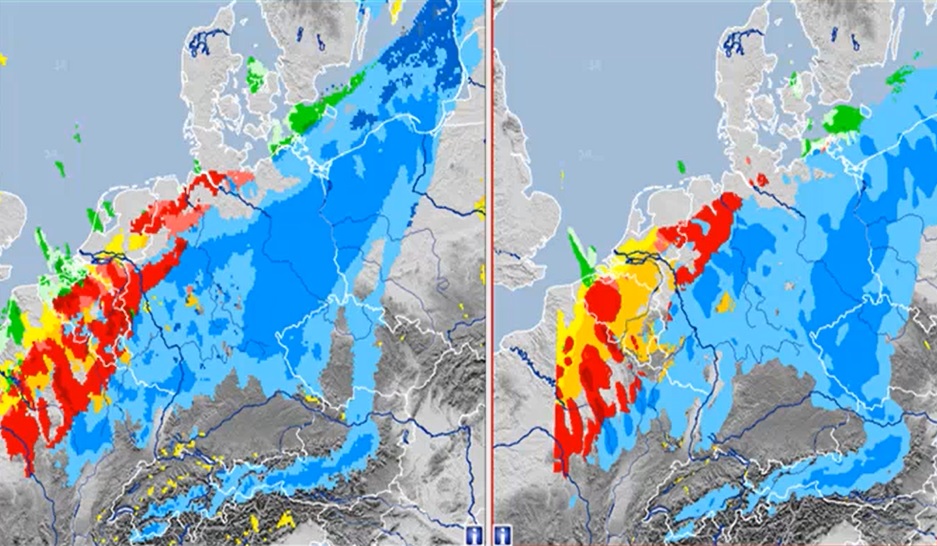
The talk of this presentation is focused on analyzing development of convective cells that may give huge amounts of precipitation. Marcus Beyer shows us the ingredient based forecasting method analyzing CAPE, moisture and lift, the three essential ingredients for developing of convection and then additionally the shear component that governs the strength of a convective cell. Later on Marcus analyzes two cases of convection that caused major damages in Germany using this method.
Presentation 1 in the Warnings Event Week 2017
Length: 35 min
Author: Thomas Kratsch (DWD)
The presentation is about the three-tiered warning system with probabilistic texts days in advance that is used in Germany. The texts consist of pre-warning information about one or two days in advance and severe weather warnings a few hours and up to 12 hours in advance. Warning thresholds for Germany and the ways of delivering these warnings to public are presented along with the software used for this process.
Length: 67 min
Author: Marko Blaskovic (DHMZ)
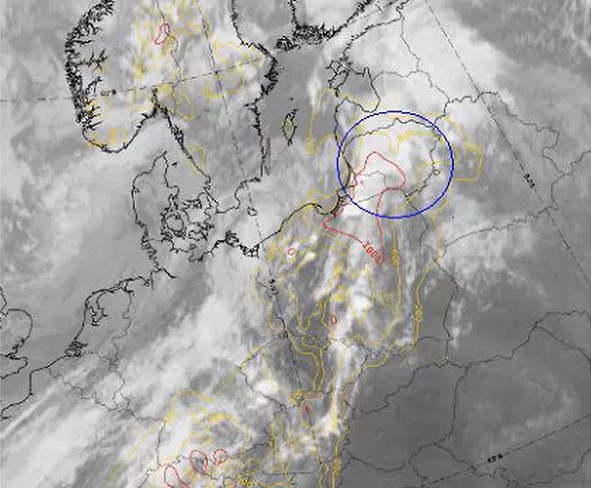
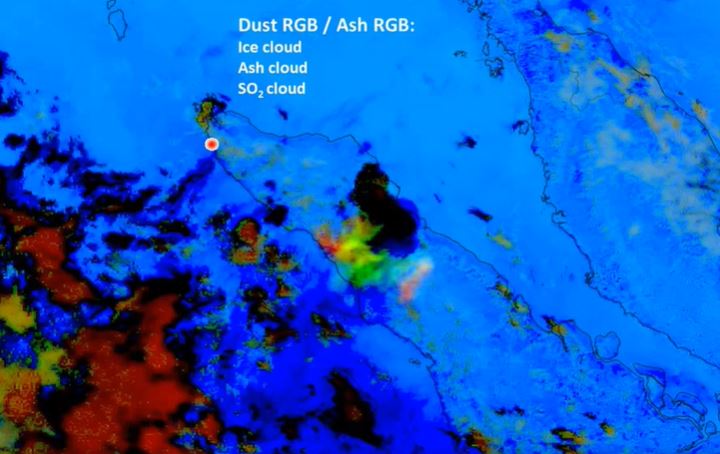
Marko Blaskovic goes through all the important atmospheric phenomena you can possibly see using satellite imagery. At the beginning the lecture treats smoke and dust with some examples and exercises. After that, ways of detecting precipitation clouds, analysing convection and pollution are shown in a couple of examples and the presentation then ends with a short overview of clear air turbulence visible from satellites.