Front intensification by jet crossing: FI by Jet
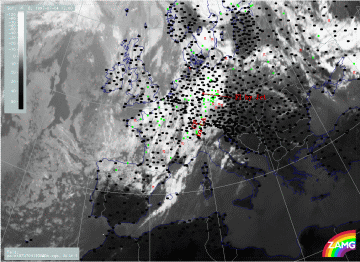
There is a period within the life-time of the frontal cloud band where cloudiness is intensified in the left exit region of a crossing jet streak. This phase is not directly associated with the cut-off development and the flood event, but as it is accompanied by many thunderstorms over a rather long period of time it results in a heavy rainfall situation already prior to the main flood situation.
In the three-hourly sequence the first sign of a cloud intensification area is over Germany, where there are already many thunderstorms. By 18.00 UTC the intensification moves eastward and a distinct cyclonic curvature develops in the cloudiness. At the same time thunderstorm activity still increases, persisting until around 00.00 UTC but becoming less numerous.
Another interesting phenomenon is the separation of the enhanced cloud part from the main frontal cloud band which can be seen best between 18.00 and 00.00 UTC. This separated part remains as a convective line and moves NE-ward to the Baltic States and White Russia, as shown on the 05/06.00 UTC image.
|
04 July 1997/12.00 UTC - Meteosat IR image; weather events (green: rain and showers, blue: drizzle, cyan: snow, red: thunderstorm with precipitation, purple: freezing rain, orange:
hail, black: no actual precipitation or thunderstorm with precipitation); 04/12.00 - 05/06.00 UTC 3-hourly image loop
|
|
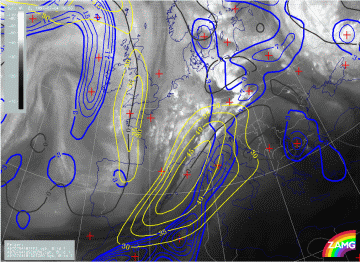
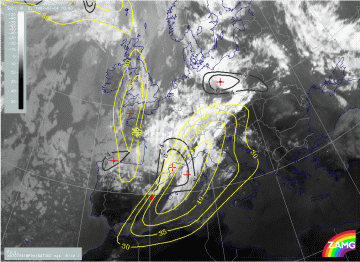
There is a pronounced jet streak parallel to the western edge of the frontal cloud band which crosses the front represented by the thermal front parameter TFP in the area of Austria - Slovakia. In the WV image some deviation between the Black Stripe and the model jet axis (zero line of shear vorticity at 300 hPa) can be observed over Italy and Austria.
There are two main PVA maxima accompanying the frontal cloud band and the jet streak area:
- One in the northern part which is the left exit region and is associated with the intensification area over E. Germany and Poland; this is typically a consequence of shear vorticity and
- One over France and NE Spain which is close to the centre of the jet streak and reaches and even overruns the jet axis, although the biggest part is on the cyclonic side; this PVA maximum is typically caused by curvature vorticity and is associated with the band feature which has developed in the cold air behind the frontal cloud band.
|
04 July 1997/18.00 UTC - Meteosat WV image; blue: thermal front parameter (TFP) 500/850 hPa, yellow: isotachs 300 hPa, black: shear vorticity 300 hPa
|
04 July 1997/18.00 UTC - Meteosat WV image; black: positive vorticity advection (PVA) 300 hPa, yellow: isotachs 300 hPa, black: shear vorticity 300 hPa
|